Here we are talking about detailed comparison from the various execution result on mentioned Gen AI models in terms of parameters like Technical Aspects, Performance and Robustness, Customization and Control, Ethical and Accessibility and User Experience and Handling of these technologies based on the following parameters. Please refer Fig01
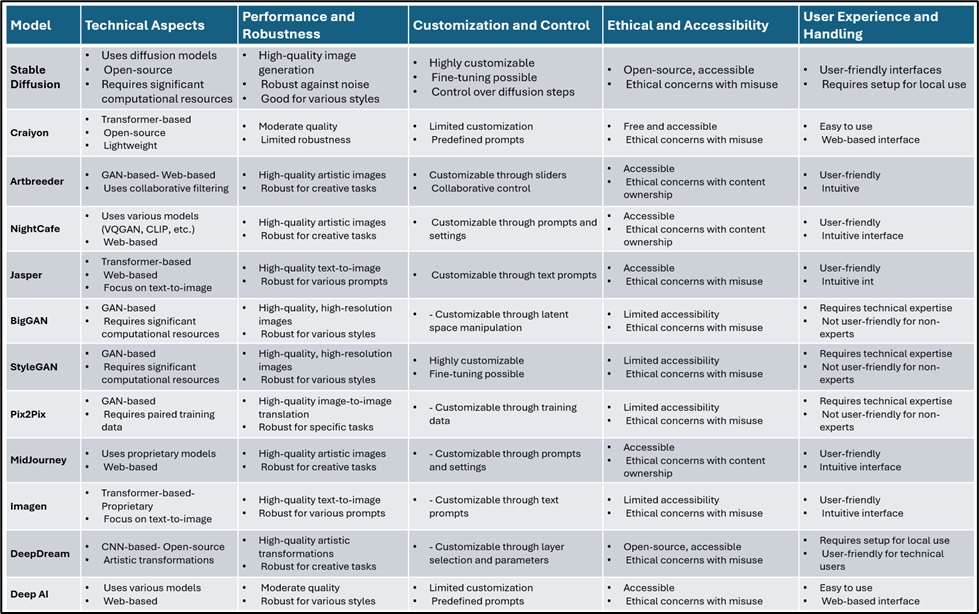
Fig 01 presents a comprehensive comparison of Gen AI models used for image creation.
Visual analysis and inference
Let us undertake a detailed comparative analysis of four distinct models: Stable Diffusion, Craiyon, Artbreeder, and NightCafe. Chosen for their broad adoption, varied technological methodologies, and distinctive features, our aim is to rigorously assess and compare each model’s performance and artistic prowess. This will be achieved by testing them against six carefully curated and demanding case scenarios, each designed to cover a broad range of visual content. This approach ensures a comprehensive evaluation of the models’ abilities. The assessment criteria will focus on image quality, consistency, artistic expression, and the precision of converting textual prompts into corresponding visual representations.
The six distinct case scenarios (Flying car, Crowd face, Joyful elephants, A robot welding, Sunrise at mountain lake, Cozy rustic kitchen) (Fig 02) were chosen for the analysis because they represent a broad spectrum of visual content.
This thorough comparative analysis is designed to illuminate the strengths and weaknesses of each model, as well as their appropriateness for various artistic and practical endeavors. By assessing their capabilities in demanding situations, we provide artists, developers, and researchers with the necessary insights to choose an image synthesis technology that best fits their unique creative or functional goals.

Fig 02 shows a comparison of images generated by AI models, created using specific prompts.
Please see the comprehensive comparison of the four models across our six test scenarios. This analysis offers valuable insights into the distinct strengths and limitations of each model, empowering users to select the most suitable technology for their specific needs and objectives, whether they are pursuing creative, practical, or research-oriented tasks.
Flying car:
- Stable Diffusion: The images were visually striking and captured the futuristic theme well, with minor issues in rendering some elements like flying cars.The cityscape was well-rendered with a futuristic look.
- Craiyon: Good overall quality with detailed cityscapes but occasional distortions in flying cars. The flying cars were present but sometimes appeared slightly distorted or out of proportion.
- Artbreeder: The images were aesthetically pleasing and creative, capturing the essence of a futuristic cityscape, but with a more artistic rather than realistic approach. Artistic and visually appealing images with well-integrated but stylized flying cars.
- Nightcafe: Nightcafe exhibited the poorest performance among the models. The cityscape lacked detail and coherence. The flying cars were either missing or poorly rendered, often blending into the background.
Crowd face
- Stable Diffusion: Poor performance with lack of detail and coherence in both faces and background. The expressions were not well-captured, often appearing unnatural or missing entirely.
- Craiyon: Vibrant and detailed images with realistic expressions and a coherent background, capturing the prompt effectively. The images were visually striking and captured the prompt well, with minor issues in rendering some elements.
- Artbreeder: Artistic and visually appealing images with well-captured expressions but more stylized than realistic. The background was present and integrated well with the faces, though it had an artistic rather than realistic look.
- Nightcafe: Good overall quality with detailed faces and expressions, though occasional distortions were present. The background of the stadium was present but sometimes lacked detail and coherence.
Joyful elephants
- Stable Diffusion: Poor performance with lack of detail and coherence in both the landscape and the animals. The elephants and other animals were poorly rendered, often blending into the background or appearing unnatural.
- Craiyon: High-quality images with detailed and vivid jungle landscapes, well-rendered elephants, and vibrant animals. The background was detailed with dense foliage and flowering trees, adding to the overall realism.
- Artbreeder: Vibrant and detailed images with realistic jungle landscapes, joyful elephants, and colorful animals, capturing the prompt effectively. The background was detailed and coherent, with dense foliage and flowering trees adding to the overall realism.
- NightCafe:. Artistic and visually appealing images with well-integrated but stylized animals and a creative jungle landscape. The elephants and other animals were well-integrated into the scene, though they sometimes appeared more stylized than realistic.
A robot welding
- Stable Diffusion: Poor performance with lack of detail and coherence in both the workshop and the robot. The images were far from realistic, with a lack of clear structure and detail in both the workshop and the robot.
- Craiyon: High-quality images with detailed and realistic workshop environments, well-rendered robots, and welding operations. The images were vivid and realistic, capturing the essence of a robot welding in a cluttered workshop.
- Artbreeder: Artistic and visually appealing images with well-integrated but stylized robots and a creative workshop environment. The robot and welding operation were well-integrated into the scene, though they sometimes appeared more stylized than realistic.
- Nightcafe: Vibrant and detailed images with realistic workshop environments, accurate robot and welding operations, capturing the prompt effectively. The robot and welding operation were depicted accurately, with sparks flying and welding residue visible on the robot’s body.
- sunrise at mountain lake
- Stable Diffusion: Not biased performance with small lack of detail and coherence in both the lake and the surrounding environment. The images were far from realistic, with a lack of clear structure and detail in both the lake and the surrounding environment.
- Craiyon: High-quality images with detailed and realistic lake environments, well-rendered surrounding elements, and integrated cabin and trees. The images were vivid and realistic, capturing the essence of a serene mountain lake at sunrise.
- Artbreeder: Artistic and visually appealing images with well-integrated but stylized elements and a creative lake environment. The images were aesthetically pleasing and creative, capturing the essence of a serene mountain lake at sunrise with a more artistic approach.
- Nightcafe: Vibrant and detailed images with realistic lake environments, accurate surrounding elements, and well-integrated cabin and deer, capturing the prompt effectively. The towering pine trees and snow-capped peaks were depicted accurately, adding to the overall realism.
Cozy rustic kitchen
- Stable Diffusion: High-quality images with detailed and realistic kitchen environments, well-rendered fireplace, wooden beams, table setting, cat, and sunlight. The table set with freshly baked bread and a pot of stew was detailed and realistic.
- Craiyon: The images were vivid and realistic, capturing the essence of a cozy, rustic kitchen. The cat curled near to fireplace and the sunlight streaming through the window with flower boxes were well-integrated into the scene.
- Artbreeder: Artistic and visually appealing images with well-integrated but stylized elements and a creative kitchen environment. The cozy, rustic kitchen ambiance was well-captured with realistic lighting.
- Nightcafe: Vibrant and detailed images with realistic kitchen environments, accurate fireplace, wooden beams, table setting, cat, and sunlight, capturing the prompt effectively. The table setting with bread and stew was present but had an artistic rather than realistic look
Discussion
We all talk about how generative AI models have the potential to revolutionize the creative industry, what are the general model algorithms and most useful Geni AI solution in the market and compared images created by it. We also need to discuss challenges as well.
The challenges associated with including Generative AI (GAI) in imaging are multifaceted and require a comprehensive approach. Let us List those and discuss them in detail in the below table. Please refer Fig 03
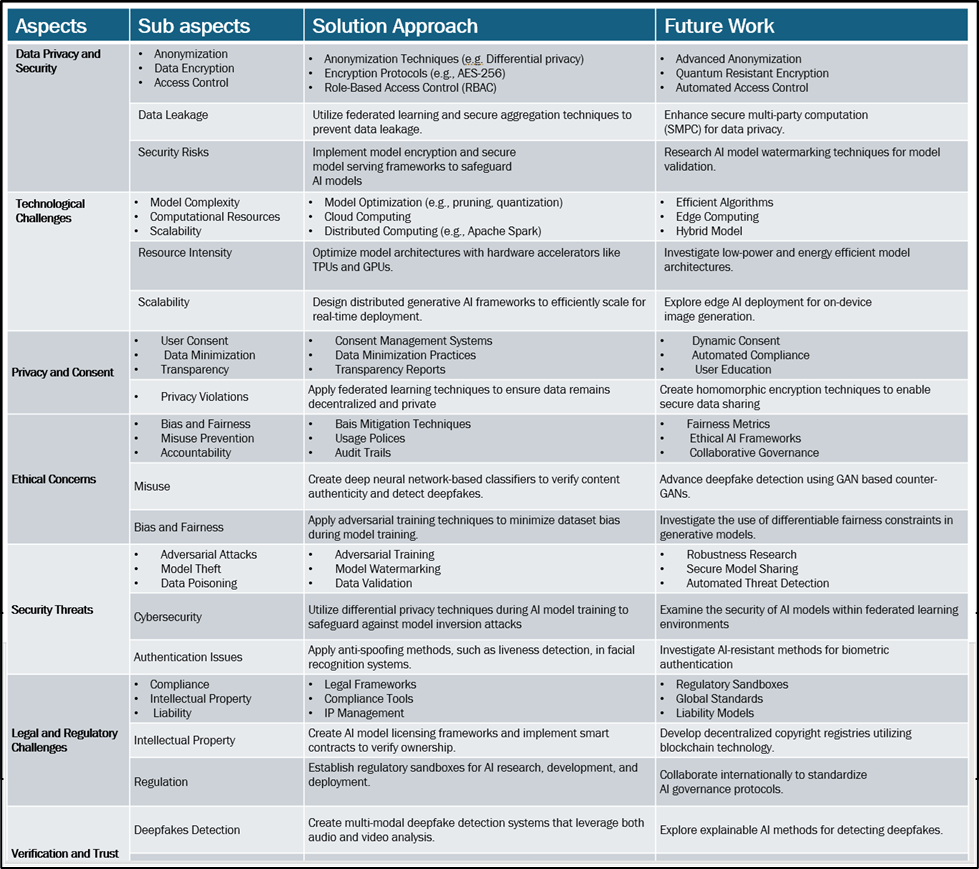
Fig 03 presents challenges in Generative AI (GAI) imaging and probable solutions
To summarize, the integration of Generative AI into imaging presents a multitude of challenges spanning ethical, privacy, security, legal, and technological aspects. Tackling these issues necessitates a comprehensive strategy that includes technical solutions, continuous research, and interdisciplinary and international cooperation.
Future Directions
The advancement of artificial intelligence has revolutionized artistic practices, leading to the creation of dynamic AI art communities dedicated to fostering collaboration and innovation. As research into generative image creation deepens, it’s crucial to consider the future trajectory of these communities. Trends suggest a growing focus on interdisciplinary collaboration, uniting artists, technologists, and academics to push the limits of creativity. This fusion of varied insights is anticipated to produce more nuanced artistic works and spur the development of novel techniques surpassing conventional approaches.
Moreover, the increasing accessibility of AI tools promises to make the creative process more democratic, allowing a wider array of people to engage with AI art communities. Progress in intuitive interfaces and open-source platforms will enable beginners and hobbyists to delve into generative AI, creating a welcoming space for education and idea exchange. This evolution will not only foster a sense of community but also propel innovation through shared creativity. These focused collectives will support concentrated research and trials, significantly contributing to the larger AI art community. By dedicating efforts to specific uses of generative AI, researchers aim to discover new methods and enhance existing ones.
As technology evolves, it is essential to remain proactive in addressing these issues and driving innovation in the field. Future improvements for generative AI in multimedia include:
AI-powered Story Weaving: Generative AI tools can assist multimedia developers in crafting their stories by generating various concept art sketches from high-level story descriptions or suggesting visually captivating multimedia that aligns with the narrative’s emotional tone. This enhances both agility and creativity in the development process.
Interpretable AI in Multimedia: Creating explainable AI techniques tailored for the multimedia domain enables users to comprehend the reasoning behind AI-generated content. This approach promotes trust and transparency.
Technological Advancements: Future efforts should aim to enhance the realism, quality, scalability, robustness, and semantic coherence of multimedia. Investigating the integration of various generative AI models (such as VAEs, GANs, Transformers, and Autoregressive Models) can spur innovation. Additionally, advancing data compression techniques will facilitate the efficient storage and transmission of multimedia content.
Countering Deepfakes and Disinformation: Research findings can guide the creation of effective deepfake detection techniques specifically designed for the multimedia field. This enables users to critically assess multimedia content and reduce the spread of misinformation.
User Behavior Analysis: Creating generative AI models that dynamically adjust to user preferences in real-time has the potential to transform multimedia content delivery. By offering personalized and customized content, we can ensure that each user gets exactly what they desire, enhancing their engagement and satisfaction.
Image synthesis technology has the potential to transform numerous fields. Here are some key areas it can influence:
Materials Science: AI can facilitate virtual testing and optimization of new material properties before they are physically created, speeding up innovation. Additionally, it plays a vital role in simulating material degradation over time, enabling non-destructive testing, preventative maintenance, and enhancements in infrastructure safety.
Medical Imaging: Image synthesis can improve early disease detection by analyzing medical scans, like mammograms, to spot subtle anomalies, resulting in better patient outcomes. Additionally, it enables doctors to simulate treatment effects on a patient’s condition, allowing for personalized treatment plans and enhancing surgical results through AI-generated 3D models of organs and tissues.
Space research: AI can enhance planetary imaging by analyzing telescope data to eliminate noise and improve images of distant planets, uncovering essential atmospheric details and the potential for life. Furthermore, AI can create simulations of Martian landscapes, supporting mission planning and astronaut training.
Conclusion
The intersection of technology and the arts within the multimedia sphere has long fascinated researchers. The advent of Generative AI marks a pivotal shift in this narrative, fundamentally altering the production of multimedia and the collaborative nature of creation. Generative AI has been a game-changer in image generation, expanding the horizons of creativity and partnership. It has not only enhanced human creative capabilities but also made the content creation process more efficient, encouraging new forms of collaboration between AI systems and human artists. The paper thoroughly examines cutting-edge Generative AI models, such as Stable Diffusion, Craiyon, Artbreeder, NightCafe, Jasper, BigGAN, StyleGAN, Pix2Pix, Midjourney, IIMAGEN, DeepDream, Deep AI, and DALL-E 2, evaluating their effectiveness in terms of image quality, diversity, interpretability, and computational efficiency. This integration of AI with image generation delves into text-to-image synthesis, where AI converts textual descriptions into compelling visual art. Nonetheless, this advancement also reveals a complex web of ethical dilemmas and challenges.
The future of AI art communities is poised for significant transformation, driven by interdisciplinary collaboration, increased accessibility, specialization, and ethical considerations. As researchers navigate this dynamic landscape, their contributions will play a vital role in shaping the trajectory of generative image creation. By embracing these future directions, AI art communities can enhance their impact on the broader artistic ecosystem, redefining the role of technology in creative expression. The ongoing dialogue between researchers, artists, and technologists will be essential in unlocking the full potential of AI as a transformative force in the world of art.

